Plants and society 8th edition – Plants and Society, 8th Edition, embarks on an illuminating journey that explores the profound relationship between plants and human civilization. From ancient origins to contemporary applications, this edition delves into the multifaceted roles that plants play in our lives, unveiling their nutritional, medicinal, industrial, cultural, and environmental significance.
As we delve deeper into the intricate tapestry of plants and society, we uncover a treasure trove of knowledge that has shaped our past, sustains our present, and holds the key to our future.
History and Evolution of Plant-Society Relationships
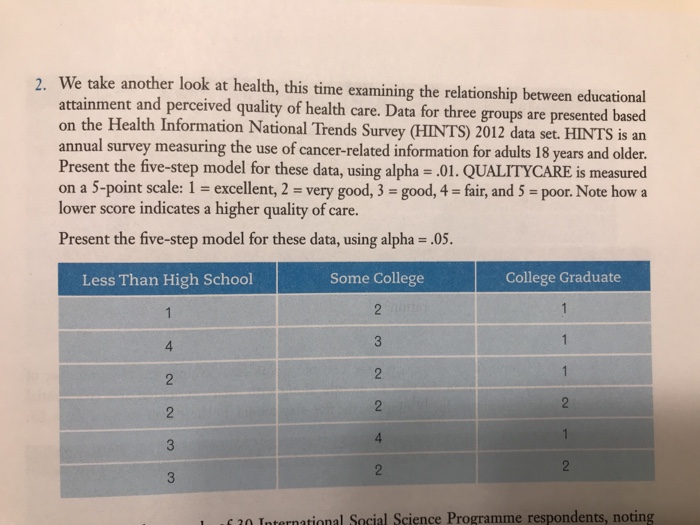
Plants have played a pivotal role in shaping human societies since the dawn of civilization. Their significance extends beyond sustenance, encompassing cultural, economic, and medicinal domains.
In ancient civilizations, plants were revered as sacred entities and integrated into religious rituals. From the lotus flower in ancient Egypt to the oak tree in Celtic culture, plants symbolized spiritual power and were believed to possess healing properties.
Cultural Roles
Plants have been integral to human cultures worldwide, influencing art, literature, and music. The lotus flower, for instance, has been depicted in Egyptian hieroglyphics and Buddhist art, symbolizing purity and enlightenment. The willow tree has inspired countless poems and songs, embodying themes of love, loss, and resilience.
Economic Roles
Throughout history, plants have been essential for economic prosperity. Crops such as wheat, rice, and maize have sustained civilizations, while timber and other plant materials have been used for construction, tools, and transportation. In modern times, plants continue to play a vital role in industries such as agriculture, forestry, and pharmaceuticals.
Medicinal Roles
Plants have been a rich source of medicinal remedies for centuries. From the willow bark used to alleviate pain to the foxglove plant used to treat heart conditions, plants have provided countless natural cures. Traditional medicine systems around the world rely heavily on plant-based treatments, and even modern medicine continues to explore the therapeutic potential of plants.
Plants as a Source of Sustenance

Plants are essential for human survival, providing the vast majority of our food. They are a rich source of nutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Plant-based foods are also generally low in calories and high in fiber, making them an important part of a healthy diet.
Nutritional Value of Plants
The nutritional value of plants varies depending on the type of plant, but all plants contain a variety of essential nutrients. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for the body, and plants are a good source of complex carbohydrates, which are slowly digested and provide sustained energy.
Proteins are essential for building and repairing tissues, and plants are a good source of plant-based proteins, which are generally lower in saturated fat than animal-based proteins.
Fats are essential for hormone production and cell function, and plants are a good source of unsaturated fats, which are healthier than saturated fats. Vitamins are essential for a variety of bodily functions, and plants are a good source of vitamins A, C, and E.
Minerals are also essential for a variety of bodily functions, and plants are a good source of minerals such as iron, calcium, and potassium.
Types of Plants Used for Food
There are a wide variety of plants that are used for food, including fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Fruits are the ripened ovaries of flowering plants, and they are typically sweet and juicy. Vegetables are the edible parts of plants, such as leaves, stems, roots, and tubers.
Grains are the seeds of grasses, and they are a good source of carbohydrates and protein. Legumes are the seeds of leguminous plants, and they are a good source of protein and fiber.
Plant-Based Diets vs. Animal-Based Diets
Plant-based diets are diets that are based primarily on plants, while animal-based diets are diets that are based primarily on animal products. There is a growing body of evidence that suggests that plant-based diets are healthier than animal-based diets. Plant-based diets have been shown to reduce the risk of heart disease, stroke, type 2 diabetes, and some types of cancer.
Plant-based diets are also generally more environmentally sustainable than animal-based diets.
Plants in Medicine and Healthcare

Plants have played a pivotal role in medicine and healthcare for millennia. They have been used in traditional medicine practices across various cultures, and modern medicine continues to harness their therapeutic properties to develop new drugs and treatments.
Plants contain a vast array of active compounds, including alkaloids, glycosides, terpenes, and flavonoids, which possess a wide range of therapeutic properties. These compounds have been shown to have antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer effects.
Medicinal Plants and Their Applications
Numerous medicinal plants have been identified and used to treat various ailments. Some notable examples include:
- Aloe vera: Used for wound healing, burns, and skin irritations due to its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties.
- Echinacea: Used to boost the immune system and reduce symptoms of colds and flu.
- Ginger: Used to relieve nausea, vomiting, and motion sickness.
- Garlic: Used for its antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties.
- Ginkgo biloba: Used to improve blood circulation and cognitive function.
- St. John’s wort: Used to treat mild to moderate depression.
These are just a few examples of the many medicinal plants that have been used for centuries to promote health and well-being.
Plants in Industry and Commerce
Plants have played a pivotal role in the development of human civilization, providing a vast array of resources for industrial and commercial purposes. From textiles to paper and building materials, plants have been instrumental in shaping the material world around us.
Beyond their practical applications, plants also hold immense economic value, contributing significantly to global trade and commerce. The pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries rely heavily on plant-based ingredients, with many products containing extracts or derivatives from various plant species.
Textiles
Natural fibers derived from plants, such as cotton, linen, and jute, have been used for centuries in the production of textiles. Cotton, obtained from the cotton plant, is the most widely used natural fiber, known for its comfort, breathability, and versatility.
Linen, extracted from the flax plant, is renowned for its strength, durability, and moisture-wicking properties.
Paper
Paper, an essential material for communication, packaging, and various other applications, is primarily made from wood pulp. Trees, such as pine, spruce, and fir, are the main sources of wood pulp, which is processed to create paper products ranging from writing paper to cardboard.
Building Materials
Wood, obtained from trees, is a widely used building material, valued for its strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. It is employed in the construction of houses, furniture, and a variety of other structures. Bamboo, a rapidly growing plant, is also gaining popularity as a sustainable building material due to its strength, flexibility, and eco-friendliness.
Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Industries, Plants and society 8th edition
Plants have been a rich source of medicinal compounds for centuries, with many modern pharmaceuticals derived from plant extracts. For instance, aspirin, a widely used pain reliever, was originally derived from the willow tree. Similarly, digitalis, used to treat heart conditions, is extracted from the foxglove plant.
The cosmetic industry also relies heavily on plant-based ingredients, with many products containing extracts or derivatives from plants such as aloe vera, green tea, and lavender. These ingredients are valued for their soothing, moisturizing, and antioxidant properties.
Plants in Environmental Conservation: Plants And Society 8th Edition
Plants play a crucial role in maintaining the health and stability of our planet’s ecosystems. They serve as the foundation of food chains, providing sustenance for countless animal species. Moreover, plants contribute significantly to biodiversity, acting as habitats for a vast array of organisms, from microscopic bacteria to large mammals.
Carbon Sequestration and Air Purification
Plants are essential in regulating the Earth’s atmosphere. Through the process of photosynthesis, they absorb carbon dioxide from the air and convert it into organic matter. This process helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate climate change. Additionally, plants release oxygen into the atmosphere, contributing to air purification and improving air quality.
Plants and Society 8th Edition provides a comprehensive overview of the dynamic relationship between plants and human societies. Its in-depth exploration of topics like plant biology, ecology, and economic botany makes it a valuable resource for students and professionals alike.
If you’re looking for additional support with your studies, be sure to check out McGraw Hill Chapter 7 Answers . These detailed explanations and practice questions will help you master the concepts presented in Plants and Society 8th Edition.
Plant-Based Conservation Efforts
The conservation of plant species is vital for preserving biodiversity and maintaining ecosystem balance. Several plant-based conservation efforts have been implemented worldwide, including:
- Reforestation and Afforestation:Planting trees in areas that have been deforested or cleared for other purposes helps restore ecosystems, increase biodiversity, and mitigate climate change.
- Protected Areas:Establishing national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and other protected areas helps preserve plant habitats and protect endangered species.
li> Botanical Gardens and Seed Banks:Botanical gardens and seed banks play a vital role in preserving plant diversity and providing a safe haven for rare and endangered species.
These conservation efforts have a significant impact on the environment, helping to maintain biodiversity, protect endangered species, and mitigate climate change. By safeguarding plant species, we are safeguarding the health and stability of our planet’s ecosystems for future generations.
Plants in Culture and Society
Plants have played a vital role in human cultures throughout history, symbolizing various aspects of life and inspiring artistic expression. Their aesthetic beauty and symbolic significance have made them integral to our social fabric.
In art, plants have been depicted in paintings, sculptures, and textiles, often representing nature, growth, and fertility. From the delicate petals of flowers to the towering trees in landscapes, plants have provided artists with a rich source of inspiration.
Use of Plants in Literature and Music
In literature, plants have been used as metaphors and symbols to convey emotions, themes, and character traits. For example, the rose is often associated with love and beauty, while the willow tree represents sorrow and loss.
In music, plants have inspired composers and musicians alike. The sounds of nature, such as rustling leaves and birdsong, have been incorporated into musical compositions, creating a sense of tranquility and connection to the natural world.
Cultural Festivals and Traditions
Many cultures around the world have festivals and traditions centered around plants. For example, the Japanese celebrate the cherry blossom season with picnics and parties, while the Chinese Lunar New Year is marked by the display of mandarin oranges and peach blossoms.
These festivals and traditions highlight the deep connection between plants and human culture, showcasing the symbolic and aesthetic significance of plants in our lives.
Helpful Answers
What are the key themes explored in Plants and Society, 8th Edition?
The edition delves into the historical, cultural, nutritional, medicinal, industrial, environmental, and cultural significance of plants in human societies.
How does the book approach the relationship between plants and human health?
The book explores the use of plants in traditional and modern medicine, discussing active compounds and therapeutic properties, providing examples of medicinal plants and their applications.
What industries are highlighted in the book’s discussion of plant use?
The book covers the use of plants in textiles, paper, building materials, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics, providing examples of plant-based products and their applications.