Introducing the Venn diagram animal vs plant cell, an insightful tool that unravels the captivating similarities and differences between these fundamental units of life. This exploration delves into the shared characteristics that unite these cells, while also highlighting the unique features that set them apart, offering a comprehensive understanding of their distinct identities.
Delving into the intricacies of cell structure, we uncover the common ground shared by animal and plant cells, providing a foundation for understanding their fundamental similarities. By examining these shared traits, we gain insights into the essential processes that govern all living organisms.
Animal vs. Plant Cell Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram is a graphical representation that shows the similarities and differences between two or more sets. In the case of animal and plant cells, a Venn diagram can help us to visualize the shared and unique characteristics of these two types of cells.
Venn Diagram Structure
A Venn diagram typically consists of two or more overlapping circles. The area where the circles overlap represents the similarities between the sets, while the areas outside the overlap represent the unique characteristics of each set.
Animal and Plant Cell Similarities
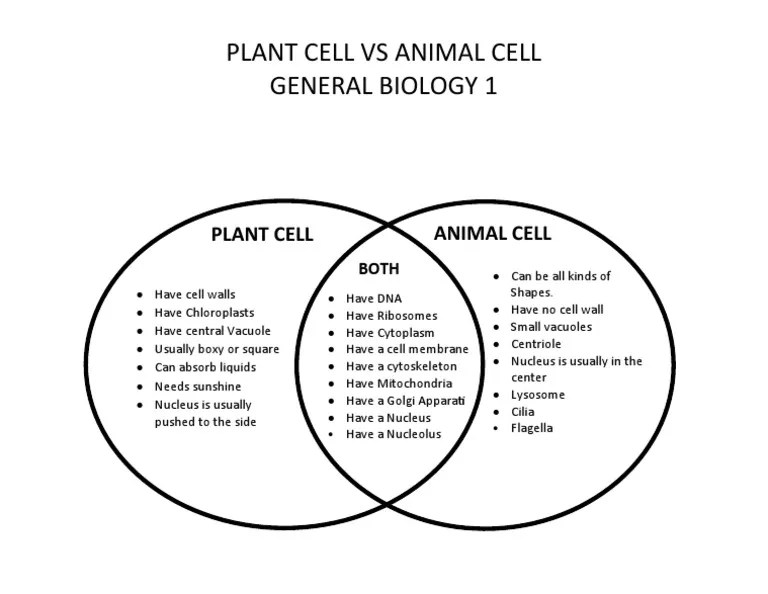
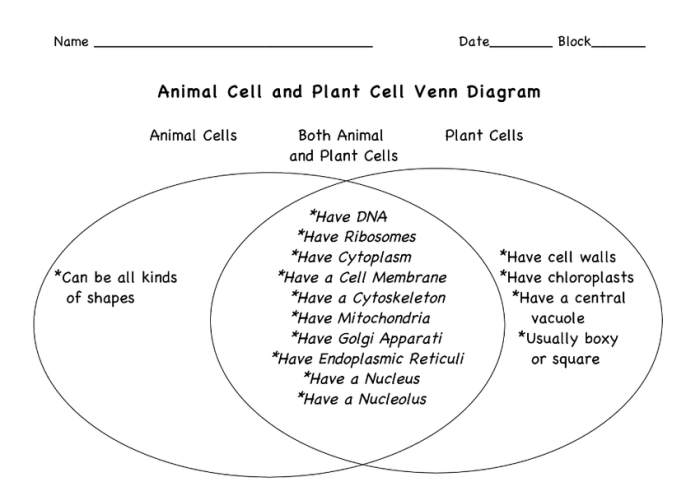
Animal and plant cells share a number of similarities, including:
- They are both eukaryotic cells, meaning that they have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
- They both have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and ribosomes.
- They both carry out the same basic cellular processes, such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
| Characteristic | Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Eukaryotic | Yes | Yes |
| Cell Membrane | Yes | Yes |
| Cytoplasm | Yes | Yes |
| Ribosomes | Yes | Yes |
| Metabolism | Yes | Yes |
| Growth | Yes | Yes |
| Reproduction | Yes | Yes |
Animal and Plant Cell Differences
Animal and plant cells also have a number of unique characteristics. Animal cells are characterized by the following:
- They have a centrosome, which is a structure that helps to organize the cell’s microtubules.
- They have lysosomes, which are organelles that contain digestive enzymes.
- They do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts.
Plant cells are characterized by the following:
- They have a cell wall, which is a rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane.
- They have chloroplasts, which are organelles that contain chlorophyll and carry out photosynthesis.
- They do not have a centrosome or lysosomes.
| Characteristic | Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Centrosome | Yes | No |
| Lysosomes | Yes | No |
| Cell Wall | No | Yes |
| Chloroplasts | No | Yes |
Examples of Animal and Plant Cells, Venn diagram animal vs plant cell
Examples of animal cells include:
- Nerve cells
- Muscle cells
- Red blood cells
- White blood cells
Examples of plant cells include:
- Leaf cells
- Stem cells
- Root cells
- Flower cells
Functions of Animal and Plant Cells
Animal cells perform a variety of functions, including:
- Movement
- Sensing the environment
- Digestion
- Reproduction
Plant cells perform a variety of functions, including:
- Photosynthesis
- Storage of nutrients
- Support
- Reproduction
| Function | Animal Cell | Plant Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Movement | Yes | No |
| Sensing the Environment | Yes | No |
| Digestion | Yes | No |
| Reproduction | Yes | Yes |
| Photosynthesis | No | Yes |
| Storage of Nutrients | No | Yes |
| Support | No | Yes |
Quick FAQs: Venn Diagram Animal Vs Plant Cell
What is the primary purpose of a Venn diagram?
A Venn diagram serves as a visual representation, illustrating the relationships between different sets of data, highlighting both their similarities and differences.
How can a Venn diagram aid in understanding the similarities and differences between animal and plant cells?
By creating separate circles for animal and plant cells, a Venn diagram effectively showcases their shared characteristics within the overlapping area, while also highlighting their unique features in the non-overlapping regions.
What are some key similarities between animal and plant cells?
Both animal and plant cells possess a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and genetic material (DNA). These shared features underscore their fundamental unity as living entities.