Carbon absorbs energy at a wavelength of 150nm, a phenomenon that unlocks a realm of scientific and technological advancements. This interaction between carbon atoms and light at this specific wavelength holds immense significance, shaping diverse applications from spectroscopy to energy conversion.
Delving into the quantum mechanical processes that govern this absorption, we explore the role of electron transitions and the factors influencing its intensity and efficiency. By understanding these mechanisms, we gain insights into the remarkable properties of carbon and its potential for transformative technologies.
Overview of Carbon Absorption at 150nm Wavelength

Carbon exhibits a distinct absorption peak at a wavelength of 150nm, a phenomenon that arises from the electronic structure of carbon atoms. This absorption is a result of the interaction between carbon’s electrons and photons of specific energy.
At 150nm, carbon atoms undergo electronic transitions from the ground state to an excited state. This transition involves the absorption of energy by the carbon atom, resulting in a decrease in the photon’s energy.
The absorption of energy at 150nm has significant implications in various scientific and technological applications, including spectroscopy, sensing, and imaging techniques. It also holds potential in energy conversion and storage technologies.
Energy Absorption Mechanism
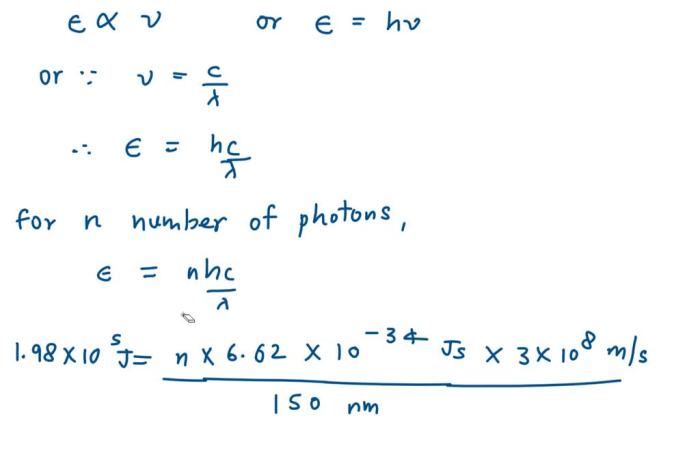
The absorption of energy at 150nm by carbon atoms is a quantum mechanical process. It involves the excitation of an electron from the 2p orbital to the 3p orbital.
The energy required for this transition corresponds to the wavelength of 150nm. The absorption intensity and efficiency depend on factors such as the concentration of carbon atoms, the temperature, and the presence of other molecules or impurities.
Applications of Carbon Absorption at 150nm
The absorption of energy at 150nm by carbon is utilized in a range of practical applications:
- Spectroscopy:Carbon absorption at 150nm is used in ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) spectroscopy to quantify the concentration of carbon in various materials.
- Sensing:Carbon-based sensors can detect specific gases and molecules by monitoring changes in absorption at 150nm.
- Imaging:Carbon absorption at 150nm is employed in imaging techniques such as carbon nanotube microscopy and graphene microscopy.
- Energy conversion and storage:Carbon-based materials are being explored for their potential in energy conversion and storage applications due to their ability to absorb energy at 150nm.
Comparison with Other Wavelengths
Carbon’s absorption at 150nm differs from its absorption at other wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum:
- Intensity:The absorption at 150nm is relatively strong compared to other wavelengths.
- Selectivity:The absorption at 150nm is specific to carbon atoms, making it a useful tool for carbon detection and analysis.
- Applications:The absorption at 150nm has unique applications in spectroscopy, sensing, and imaging, while other wavelengths are used for different purposes.
Despite its advantages, carbon absorption at 150nm also has limitations, such as potential interference from other molecules and the need for specialized instrumentation.
Experimental Techniques for Studying Carbon Absorption: Carbon Absorbs Energy At A Wavelength Of 150

Several experimental techniques are used to measure and analyze carbon absorption at 150nm:
- UV-Vis spectroscopy:This technique measures the absorption of light at different wavelengths, including 150nm, to determine the concentration of carbon in a sample.
- Fluorescence spectroscopy:This technique measures the emission of light by carbon atoms after absorbing energy at 150nm.
- Atomic absorption spectroscopy:This technique measures the absorption of light by carbon atoms in a flame or furnace.
These techniques provide valuable insights into the absorption properties of carbon at 150nm and are used in various research studies.
Future Directions and Research Opportunities

Research on carbon absorption at 150nm continues to expand, with potential future applications in:
- Advanced sensing technologies:Developing highly sensitive and selective sensors for carbon-based materials.
- Energy storage and conversion:Exploring carbon-based materials for efficient energy storage and conversion devices.
- Quantum computing:Investigating the use of carbon absorption at 150nm for quantum computing applications.
Ongoing research efforts and emerging technologies aim to advance our understanding and utilization of carbon absorption at 150nm.
FAQ Explained
What is the significance of carbon absorption at 150nm?
Carbon absorption at 150nm provides valuable insights into the electronic structure and bonding characteristics of carbon materials, enabling the development of advanced materials for various applications.
How does carbon’s absorption of energy at 150nm differ from other wavelengths?
Carbon’s absorption at 150nm exhibits unique characteristics in terms of intensity, selectivity, and applications, making it particularly suitable for specific spectroscopic techniques and energy-related technologies.
What are the potential future applications of carbon absorption at 150nm?
Ongoing research explores the potential of carbon absorption at 150nm in areas such as quantum computing, advanced imaging techniques, and the development of efficient solar cells and energy storage devices.