Correctly label the following parts of the large intestine – Correctly labeling the parts of the large intestine is crucial for understanding its anatomy and function. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the large intestine, its various segments, and their respective roles in the digestive process.
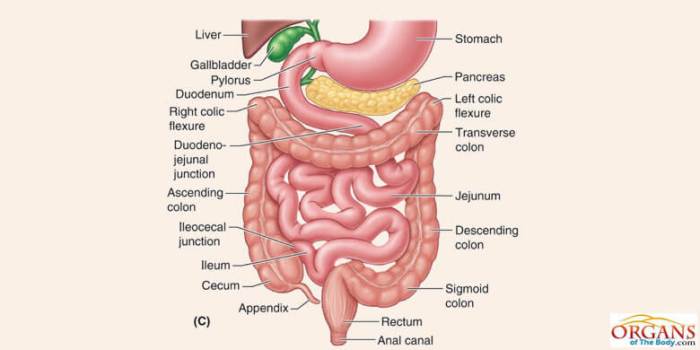
The large intestine, also known as the colon, plays a vital role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients, water, and electrolytes. It consists of several distinct segments, each with unique characteristics and functions.
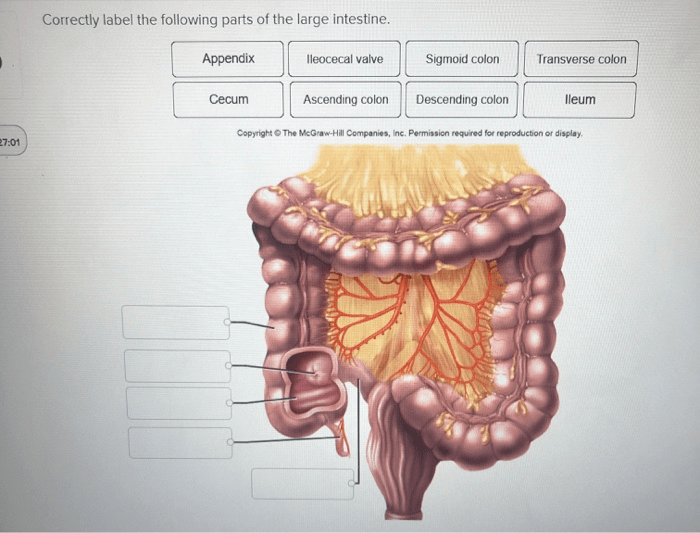
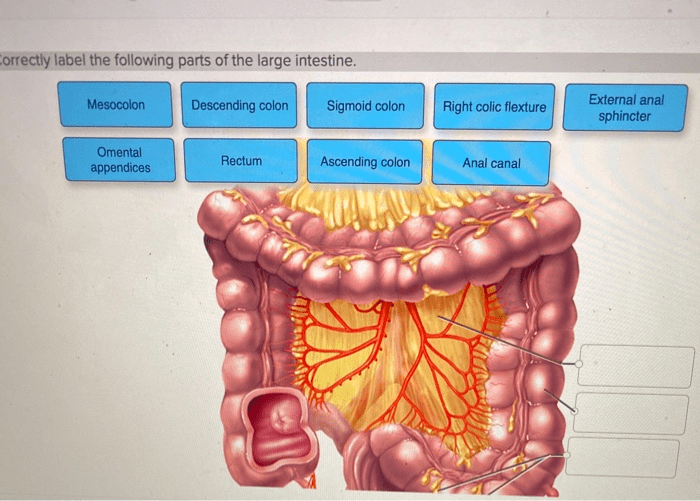
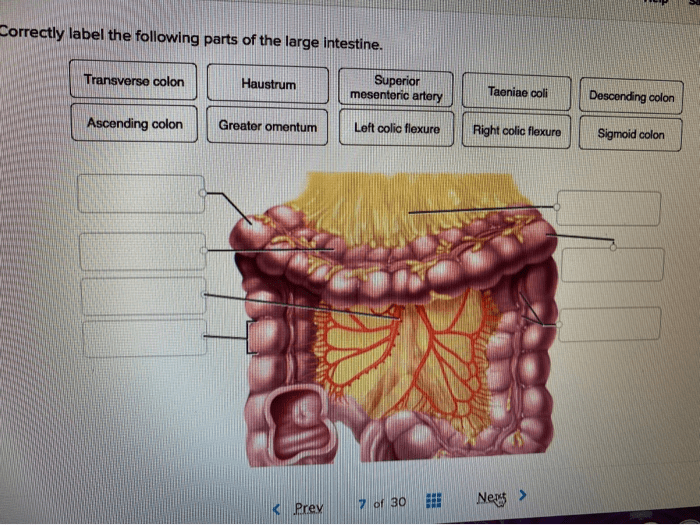
1. Define and Label Parts of the Large Intestine: Correctly Label The Following Parts Of The Large Intestine
The large intestine, also known as the colon, is the final part of the digestive system. It is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes from the digested food, storing waste products, and producing and absorbing vitamins.
| Part | Location | Function | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cecum | Where the small intestine connects to the large intestine | Receives waste from the small intestine and begins the process of water absorption | [Image of the cecum] |
| Ascending colon | Extends from the cecum to the right side of the abdomen | Continues to absorb water and electrolytes | [Image of the ascending colon] |
| Transverse colon | Crosses the abdomen from right to left | Absorbs water and stores waste | [Image of the transverse colon] |
| Descending colon | Extends from the transverse colon to the left side of the abdomen | Continues to absorb water and electrolytes | [Image of the descending colon] |
| Sigmoid colon | Forms an S-shape in the lower left abdomen | Stores waste and prepares it for elimination | [Image of the sigmoid colon] |
| Rectum | The final portion of the large intestine | Stores waste until it is eliminated | [Image of the rectum] |
| Anal canal | The last part of the digestive system | Allows waste to be expelled from the body | [Image of the anal canal] |
FAQ Overview
What is the function of the cecum?
The cecum is a pouch-like structure that receives waste material from the small intestine. It contains bacteria that help break down cellulose and other indigestible substances.
What is the role of the ascending colon?
The ascending colon absorbs water and electrolytes from the waste material, making it more solid.
What is the function of the transverse colon?
The transverse colon continues to absorb water and electrolytes, further solidifying the waste material.