As what happens when the atoms of a substance are regrouped takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Delving into the heart of chemistry, physics, and materials science, we embark on an exploration of the fundamental processes that govern the behavior of matter at its most basic level.
The content of the second paragraph that provides descriptive and clear information about the topic
Atomic Regrouping: Its Impact on Substance Properties: What Happens When The Atoms Of A Substance Are Regrouped
Atomic regrouping is a fundamental process that can lead to significant changes in the properties of a substance. This process involves the rearrangement of atoms within a substance, resulting in the formation of new substances or materials with distinct characteristics.Atomic
regrouping can occur in a variety of ways, including chemical reactions, phase transitions, and crystal structure formation. In each case, the rearrangement of atoms can have a profound impact on the substance’s properties, such as its chemical reactivity, physical state, and material strength.
Chemical Reactions
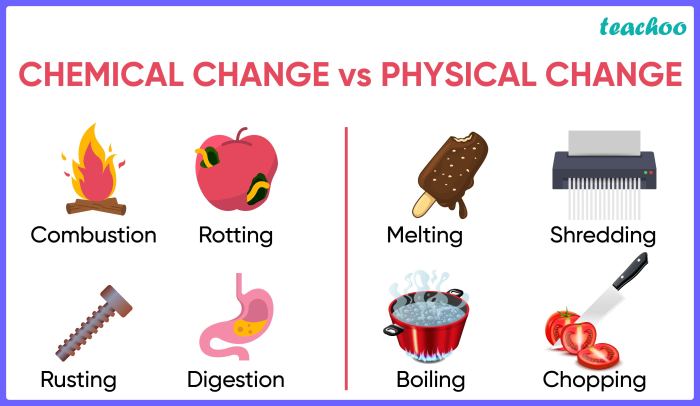
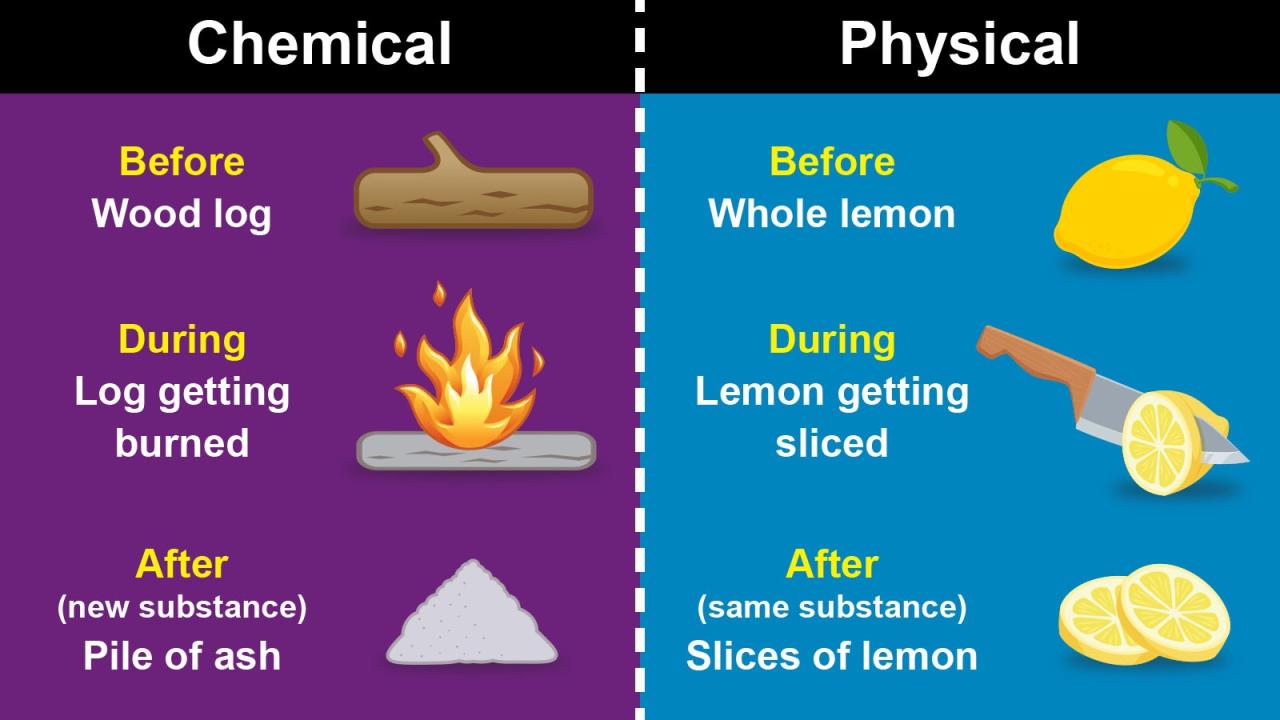
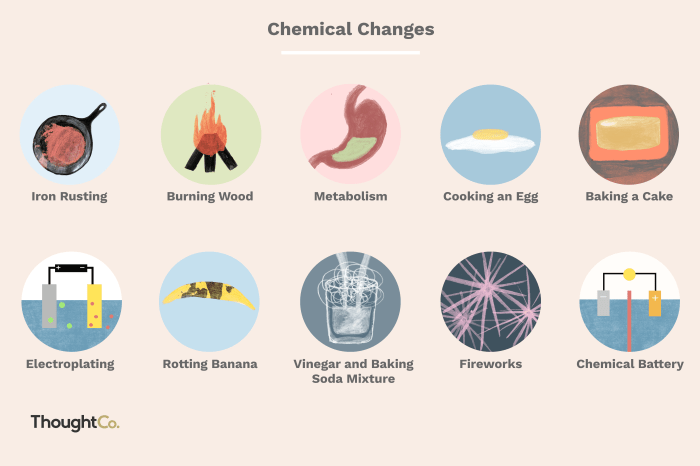
Chemical reactions are processes in which atoms are regrouped to form new substances. During a chemical reaction, the atoms of the reactants are rearranged to form the atoms of the products. This rearrangement can result in changes in the chemical properties of the substances involved.
For example, a chemical reaction can change a substance from being reactive to being inert or from being soluble to being insoluble.The energy released or absorbed during a chemical reaction is related to the rearrangement of atoms. When atoms are brought together to form new bonds, energy is released.
When atoms are separated to break bonds, energy is absorbed.
Phase Transitions
Phase transitions are processes in which a substance changes from one phase to another. The three main phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas. During a phase transition, the atoms of a substance are rearranged to form a new phase.
This rearrangement can result in changes in the physical properties of the substance, such as its density, melting point, and boiling point.The temperature and pressure of a substance can affect the phase transition that occurs. For example, when a solid is heated, it will eventually melt and become a liquid.
When a liquid is cooled, it will eventually freeze and become a solid.
Crystal Structures
Crystal structures are the arrangements of atoms in a solid. The arrangement of atoms in a crystal structure can affect the properties of the solid, such as its hardness, strength, and electrical conductivity. There are many different types of crystal structures, each with its own unique properties.The
arrangement of atoms in a crystal structure is determined by the forces between the atoms. These forces can be ionic, covalent, or metallic. Ionic bonds are formed between positively and negatively charged ions. Covalent bonds are formed between atoms that share electrons.
Metallic bonds are formed between atoms that are surrounded by a sea of electrons.
Molecular Geometry, What happens when the atoms of a substance are regrouped
Molecular geometry is the arrangement of atoms in a molecule. The molecular geometry of a molecule can affect its properties, such as its reactivity, solubility, and boiling point. There are many different molecular geometries, each with its own unique properties.The
molecular geometry of a molecule is determined by the number of atoms in the molecule and the types of bonds between the atoms. For example, a molecule with two atoms will have a linear molecular geometry. A molecule with three atoms will have a trigonal planar molecular geometry.
A molecule with four atoms will have a tetrahedral molecular geometry.
Bonding
Bonding is the process by which atoms are held together to form molecules and compounds. There are many different types of bonds, each with its own unique properties. The type of bond that forms between two atoms depends on the atoms’ electronegativities.
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons.The most common type of bond is the covalent bond. A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share electrons. Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers electrons to another atom.
Metallic bonds are formed when metal atoms share electrons in a sea of electrons.
Materials Science
Materials science is the study of the properties of materials and how they can be used to create new materials with desired properties. Atomic regrouping is a key process in materials science. By controlling the atomic regrouping process, scientists can create materials with specific properties, such as high strength, low weight, and high electrical conductivity.There
are many different techniques that can be used to control atomic regrouping. These techniques include heat treatment, cold working, and chemical vapor deposition. Heat treatment is a process in which a material is heated to a high temperature and then cooled slowly.
Cold working is a process in which a material is deformed at a low temperature. Chemical vapor deposition is a process in which a material is deposited from a gas onto a substrate.
Question Bank
What is atomic regrouping?
Atomic regrouping refers to the rearrangement of atoms within a substance, leading to changes in its chemical and physical properties.
How does atomic regrouping occur?
Atomic regrouping can occur through various processes, including chemical reactions, phase transitions, and the formation of new crystal structures.
What are the effects of atomic regrouping?
Atomic regrouping can result in the formation of new substances with different properties, changes in molecular geometry, and the creation of materials with tailored structures.