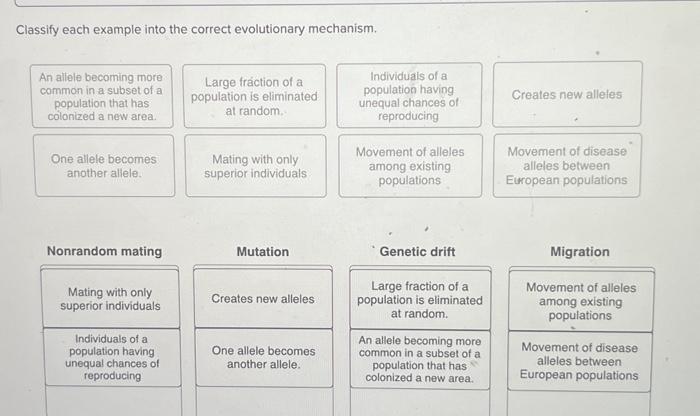
As we delve into the intricate world of evolution, it becomes imperative to classify each example into the correct evolutionary mechanism. This process enables us to comprehend the diverse forces that have shaped the tapestry of life on Earth, from the majestic whales to the humble bacteria.
By understanding these mechanisms, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and adaptability of living organisms.
Evolution, the gradual transformation of species over time, is driven by a multitude of mechanisms. Natural selection, the driving force behind adaptation, favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success. Genetic drift, the random fluctuation of gene frequencies within a population, can lead to significant changes over time.
Gene flow, the transfer of genes between populations, introduces new genetic material and can influence the genetic makeup of a species.
1. Define Evolutionary Mechanisms
Evolution is the process by which the genetic composition of a population changes over time. Evolutionary mechanisms are the processes that drive this change. These mechanisms include natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination.
2. Natural Selection: Classify Each Example Into The Correct Evolutionary Mechanism

Natural selection is the process by which individuals with traits that are better suited to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. This leads to the accumulation of favorable traits in the population over time.
3. Genetic Drift
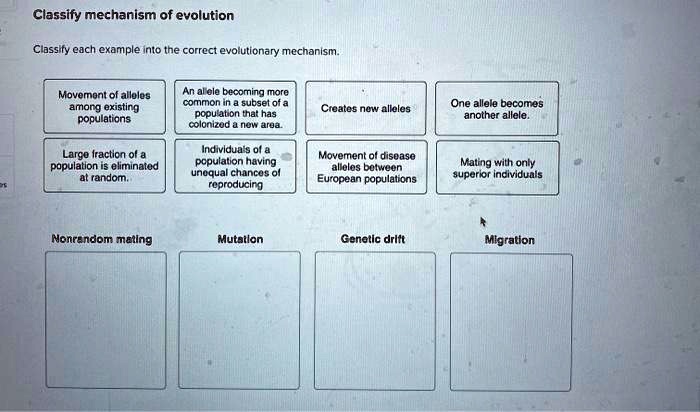
Genetic drift is the random change in the genetic composition of a population due to chance events. This can lead to the loss of genetic variation and the fixation of harmful alleles.
4. Gene Flow
Gene flow is the movement of genes into or out of a population. This can occur through migration, breeding, or other means. Gene flow can introduce new alleles into a population and increase genetic variation.
5. Mutation
Mutation is the random change in the DNA sequence of an organism. Mutations can be harmful, beneficial, or neutral. Beneficial mutations can lead to the evolution of new traits and adaptations.
6. Recombination
Recombination is the process by which genetic material is exchanged between homologous chromosomes. This can lead to the creation of new combinations of alleles and increase genetic variation.
7. Examples of Evolutionary Mechanisms
| Type of Mechanism | Example | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Selection | Peppered moths | Peppered moths that were better camouflaged against the soot-covered trees during the Industrial Revolution were more likely to survive and reproduce, leading to an increase in the frequency of the dark-colored allele in the population. |
| Genetic Drift | Founder effect | When a small group of individuals from a larger population establishes a new population, the genetic variation in the new population is likely to be reduced due to the limited number of individuals that founded it. |
| Gene Flow | Migration | The migration of individuals from one population to another can introduce new alleles into the recipient population and increase genetic variation. |
| Mutation | Sickle cell anemia | A mutation in the hemoglobin gene leads to the production of a defective form of hemoglobin that causes sickle cell anemia. This mutation can be beneficial in areas where malaria is common, as it provides some resistance to the disease. |
| Recombination | Meiosis | During meiosis, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material, leading to the creation of new combinations of alleles. |
8. Conclusion
Evolutionary mechanisms are the processes that drive the evolution of life. These mechanisms include natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for understanding the diversity of life on Earth.
Common Queries
What is the difference between natural selection and genetic drift?
Natural selection is a non-random process that favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success, while genetic drift is a random process that can lead to significant changes in gene frequencies within a population, even if those changes are not beneficial.
How does gene flow contribute to evolution?
Gene flow introduces new genetic material into a population, which can increase genetic diversity and influence the genetic makeup of the species.